Introduction:
Social Security Numbers (SSNs) play a crucial role in the identification and documentation of individuals within the United States. Originally introduced as part of the Social Security Act of 1935, these nine-digit numbers have evolved into a fundamental component of various administrative, financial, and governmental processes. In this fullz info, we will explore the significance of Social Security Numbers, their structure, and the measures taken to ensure their security.
I. Purpose of Social Security Numbers:
The primary purpose of assigning Social Security Numbers is to track individuals for Social Security benefits and related programs. Over the years, SSNs have become a key identifier in various aspects of life, including employment, taxation, healthcare, and financial transactions. Employers use SSNs for tax reporting, and financial institutions require them for opening accounts and conducting credit checks. Additionally, healthcare providers use SSNs to verify patient identities and process insurance claims.
II. Structure of Social Security Numbers:
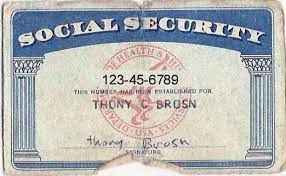
A standard Social Security Number is a nine-digit sequence divided into three parts: the first three digits represent the area number, the next two digits are the group number, and the final four digits make up the serial number. The area number reflects the state or territory where the SSN was issued, while the group and serial numbers are assigned in a specific pattern.
III. Security Measures:
Given the sensitive nature of the information associated with Social Security Numbers, protecting them from unauthorized access and potential misuse is crucial. The Social Security Administration (SSA) and other entities involved in the issuance and use of SSNs have implemented several security measures to safeguard individuals’ personal information.
- Secure Issuance Process:
- The SSA follows a secure and controlled process for assigning SSNs, ensuring that the numbers are issued only to eligible individuals.
- Restricted Access:
- Access to Social Security Numbers is limited to authorized personnel, and strict regulations are in place to prevent unauthorized disclosure.
- Secure Transmission:
- When SSNs are transmitted electronically, secure encryption methods are employed to protect the information from interception by unauthorized parties.
- Education and Awareness:
- Public awareness campaigns aim to educate individuals about the importance of safeguarding their SSNs and being cautious about sharing them, particularly in online settings.
- Identity Verification:
- Many organizations use additional identity verification methods, such as multi-factor authentication, to ensure that the person providing the SSN is the legitimate owner.
Conclusion:
Social Security Numbers are a fundamental aspect of modern life in the United States, serving as a unique identifier for individuals in various administrative, financial, and governmental processes. While they play a crucial role in facilitating these activities, it is equally important to prioritize the security and protection of SSNs to prevent identity theft and unauthorized access. By understanding the significance of SSNs and the measures in place to ensure their security, individuals can contribute to maintaining the integrity of this essential identification system.